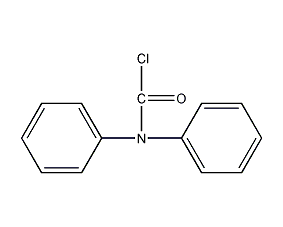
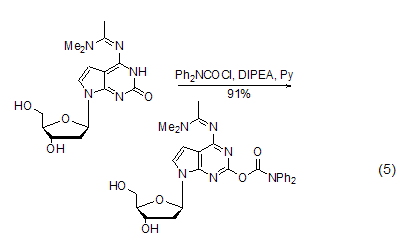
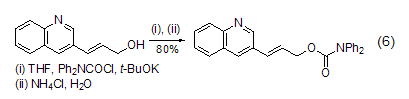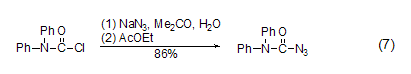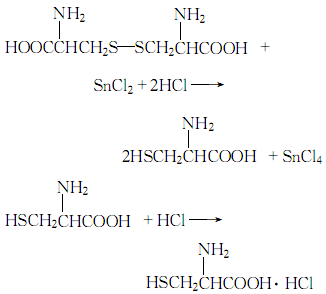Structural formula
| Business number | 015S |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H7NO2S |
| Molecular weight | 121.16 |
| label |
L-hemibladder amino acid, L-beta-mercaptoalanine, L-2-amino-3-mercaptopropionic acid, L-Hydrosulfide aminopropionic acid, (R)-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropionic acid, Thioserine, Detoxification and anti-inflammatory drugs, Intermediates |
Numbering system
CAS number:52-90-4
MDL number:MFCD00064306
EINECS number:200-158-2
RTECS number:HA1600000
BRN number:1721408
PubChem number:24901592
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless crystals, slightly odorous.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4?): Undetermined
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 240? (decomposition)
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, 13.33kpa ):
7. Refractive index: Not determined
8. Flash point (ºC): Not determined
9. Specific rotation (º,): 8.75° (c=12, 2N HCl).
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Not determined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Not determined
12. Saturation Vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (% , V/V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: soluble in water, alcohol, ammonia and acetic acid , insoluble in ether, benzene, acetone, ethyl acetate, carbon disulfide and carbon tetrachloride.
Toxicological data
Acute toxicity:
Oral LD50 660mg/kg(mus)
1890mg/kg(rat)
Main irritant effects:
On skin: Irritation to skin and mucous membranes.
On the eyes: Irritation effects.
Sensitization: No known sensitizing effects.
Ecological data
General Notes
Water Hazard Level 1 (German Regulation? (Self-assessment via list) This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Do not allow undiluted or large amounts of product to come into contact with groundwater, waterways or sewage systems.
Do not discharge materials into the surrounding environment without government permission.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 28.90
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 90.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 251.5
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 58.9
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 11.45 p>
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 3
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 64.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 75.3
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 1
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Irritating. Its aqueous solution or slightly alkaline aqueous solution can be oxidized into cystine by air, and the acidic solution is relatively stable. The biochemical reagent content is not less than 98.5%
2. Exists in tobacco leaves.
Storage method
Should be sealed and stored in a dry place away from light.
Synthesis method
1. Tin particle reduction method Dissolve cystine in dilute hydrochloric acid, filter, add tin particles to the filtrate, heat and reflux for 2 hours. Dilute the reducing solution with water, remove the remaining tin particles, add hydrogen sulfide to saturate it, filter it, wash the filter residue with a small amount of water, combine the washing and filtrate, concentrate under reduced pressure, cool and crystallize, filter and dry to obtain L-cysteine ??salt Acid.
2. Electrolytic reduction method Add distilled water, hydrochloric acid, and cystine to the electrolytic tank, stir and dissolve, and maintain the electrolysis below 50°C until the end point. The resulting electrolyte was passed through hydrogen sulfide for several hours and then filtered. The filtrate is decolorized by adding activated carbon, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, crystallized by cooling, filtered, and dried to obtain L-cysteine ??hydrochloride.
3. Synthesis: It can be made by hydrolyzing protein (such as human hair) with hydrochloric acid, then treating it with copper oxide, and decomposing it with hydrogen sulfide. It can also be derived from the degradation of cystine.
Purpose
1. Mainly used in medicine, cosmetics, biochemical research, etc. Used in bread ingredients to promote gluten formation, fermentation, mold release, and prevent aging. Used in natural juices to prevent vitamin C from oxidizing and preventing juices from turning brown. This product has detoxification effect and can be used for acrylonitrile poisoning and aromatic acid poisoning. This product also has the function of preventing radiation damage to the human body, and is also a drug for treating bronchitis, especially as a phlegm-reducing drug (mostly used in the form of acetyl L-cysteine ??methyl ester). In cosmetics, it is mainly used in beauty water, Perm liquid, sun protection cream, etc.
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1862extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/8.jpgextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/metal-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/jeffcat-td-33a-catalyst-cas107-16-9-huntsman/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Jeffcat-ZF-22-MSDS.pdfextended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/catalyst-dabco-8154-acid-blocked-tertiary-amine-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/974extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/690extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44765extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dibutyl-stannane-diacetate/