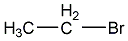
Structural formula
| Business number | 01HR |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2H5Br |
| Molecular weight | 108.97 |
| label |
Ethyl bromide, Ethyl bromide, Bromoethane, Bromoethane, Ethyl bromide, Aliphatic halogenated derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:74-96-4
MDL number:MFCD00000232
EINECS number:200-825-8
RTECS number:KH6475000
BRN number:1209224
PubChem number:24854383
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless and volatile liquid [1]
2. Melting point (?): -119[2]
3. Boiling point (?): 38.4[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 1.45 (25?)[4 ]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 3.76[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 53.2 (20?)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1423.3[7]
8. Critical temperature (?): 776.8[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 6.23[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.61[10]
11. Flash point (?): -23[11]
12. Ignition temperature (?): 511[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 11.3[12]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 6.7[14]
15. Solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol and ether and most organic solvents. [15]
16. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.507
17. Critical volume (cm 3·mol-1): 215
18. Critical compression factor: 0.320
19. Eccentricity factor: 0.183
20. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 18.475
21. van der Waals area (cm 2·mol-1): 5.550×109
22. van der Waals volume (cm 3·mol-1): 38.300
23. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1) : -91.8
24. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 100.5
25. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -63.6
26. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1 sup>·K-1): 287.36
27. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -25.7
28. Vapor phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 64.23
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 1350mg/kg (rat oral)
LC50 : 72386mg/m3 (mouse inhalation, 1h)
2. Irritation No information available
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data yet
2. Biodegradability[17] MITI-I test , the initial concentration is 100ppm, the sludge concentration is 30ppm, and the degradation is 13%~45% after 4 weeks.
3. Non-biodegradability[18] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3, the degradation half-life is 46d ( theory). At 25°C, when the pH value is 7, the hydrolysis half-life is 30 days (theoretical).
4. Other harmful effects[19] This substance is harmful to the environment. Special attention should be paid to the pollution of water bodies. .
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 19.04
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 74.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 163.8
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 23.1
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3 ):
7. Polarizability: 7.55
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.4
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 3
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 2.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Ethyl bromide is a sweet-tasting flammable liquid that easily decomposes under light or flame to produce hydrogen bromide and carbonyl bromide, the latter of which has highly toxic effects similar to phosgene.
2. React with strong alkali to generate ethylene, which is hydrolyzed in weak alkali to generate ethanol.
3. Stability[20] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[21] Strong alkali, strong oxidizing agent, magnesium
5. Conditions to avoid contact [22] Heat and light p>
6. Polymerization hazard[23] No polymerization
7. Decomposition products[24] sup> Hydrogen bromide
Storage method
Storage Precautions[25] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the reaction of ethanol and sodium bromide: Add 40% sodium bromide solution and ethanol into the reaction pot, add sulfuric acid while stirring, and the temperature should not exceed 50°C. After addition, react at 45-50°C for 2 hours. Distill, neutralize the distillate with 3% sodium carbonate solution, and let it stand for 2 hours to separate the organic phase into ethyl bromide. Raw material consumption quota: ethanol (95%) 557kg/t, hydrobromic acid (48%) 1610kg/t, sulfuric acid (92%) 1165kg/t.
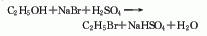
2. From ethanol and bromine Obtained from the reaction: Slowly add bromine to the suspension of sulfur and water while stirring, keeping the temperature at 35-40°C. Then add ethanol. Add sulfuric acid at 25-28°C and react for 42 hours. Distill and collect the 38-39°C fraction to obtain bromoethane. The yield is about 90%. Raw material consumption quota: ethanol 770kg/t, bromine 250kg/t, sulfuric acid 1042kg/t, sulfur 18kg/t. In method (1), you can also use hydrobromic acid and ethanol to react. The preparation process is the same as the sodium bromide method, and the yield is 96%. In addition, it can be obtained by the addition of ethylene and hydrogen bromide or by bromination of ethane. Ethyl bromide. The purity of industrial bromoethane is ?98%.
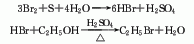
3. Use industrial product ethyl bromide Alkane is used as raw material, washed several times with concentrated sulfuric acid, once with water, twice with 10% sodium carbonate solution, once with 5% sodium thiosulfate solution, let stand to separate the aqueous layer, and wash with anhydrous chlorine After drying the calcium oxide, it is distilled and the 37-40°C fraction is collected as the finished product.
4. Preparation method:

In a reaction flask equipped with a stirrer, dropping funnel, and distillation device, add 41.5g (2.81mol) of 48% hydrobromic acid, cool in a water bath, and slowly add 120g (65mL) of concentrated sulfuric acid while stirring. , then add 100g (2.06mol) of 95% ethanol (2), heat slowly, and add 109mL of concentrated sulfuric acid dropwise from the dropping funnel, while steaming out the generated bromoethane. The connecting tube extends into the receiving bottle under the water surface, and the receiving bottle is cooled with ice water. Stop the reaction when no bromoethane evaporates. Separate the crude ethyl bromide from the distillate, wash with water, 5% sodium carbonate solution, water in sequence, and dry over anhydrous calcium chloride. Heating and distilling in a water bath, collecting the fraction at 38-39°C to obtain 205g of bromoethane (1), with a yield of 91%. [27]
5. Preparation method:
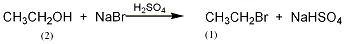
Add 100mL (1.7mol) of 95% ethanol (2) and 90mL of water into the reaction bottle. Slowly add 190mL of concentrated sulfuric acid while stirring continuously. The reaction is exothermic. Be sure to cool to room temperature. Slowly add 163g (1.5mL) of finely ground sodium bromide and a few grains of zeolite while stirring. Install the distillation device and add an appropriate amount of ? to the receiving bottle.of water and place it in an ice bath. Heat slowly to allow the reaction and distillation to proceed smoothly until no oil is distilled out. The organic layer was separated and dried with sulfuric acid. Distill and collect the fractions at 35-40°C to obtain 100-120g of bromoethane (1) with a yield of 61%-74%. [28]
Purpose
1. It is an important raw material for organic synthesis. In agriculture, it is used as a fumigation pesticide for grain storage, warehouses and buildings. Ethyl bromide is produced by reacting potassium bromide with chilled sulfuric acid and ethanol. Commonly used in ethylation of gasoline, refrigerants and anesthetics. Therefore, both chemical production workers and fumigators can be exposed to varying concentrations of ethyl bromide.
2. Ethyl bromide is a raw material for making barbiturates. It is also used as a refrigerant, anesthetic, solvent, fumigant, organic synthesis, etc.
3. Used as analytical reagents, such as solvents and refractive index standard samples. It is also used as a fire extinguishing agent in organic synthesis and aviation industry.
4. Used in organic synthesis, as solvent, refrigerant, and in the pharmaceutical industry. [26]
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Pentamethyldiethylenetriamine-CAS3030-47-5-Jeffcat-PMDETA.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/-DC2-delayed-catalyst–DC2-delayed-catalyst–DC2.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/fomrez-ul-1-strong-gel-catalyst-momentive/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/polyurethane-gel-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/u-cat-2313-catalyst-cas9733-28-3-sanyo-japan/extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/delayed-catalyst-8154-polyurethane-catalyst-8154/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/6extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44677extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/category/product/page/12/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/14.jpg