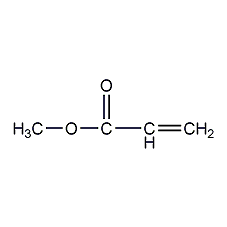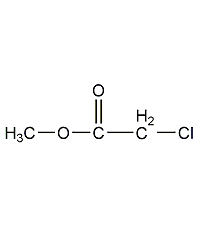
Structural formula
| Business number | 02B0 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H5ClO2 |
| Molecular weight | 108.52 |
| label |
Methyl chloroacetate;, Chloro acetic acid methyl ester, Pesticide intermediates; aliphatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:96-34-4
MDL number:MFCD00000931
EINECS number:202-501-1
RTECS number:AF9500000
BRN number:506255
PubChem number:24862524
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless and transparent liquid with pungent odor. [1]
2. Melting point (?): -32.1[2]
3. Boiling point (?): 129.8[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.24[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 3.8[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 1.33 (29?)[6]
7. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.5[7]
8. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.63[8]
9. Flash point (?): 50.15[9]
10. Ignition temperature (?): 463[10 ]
11. Explosion upper limit (%): 18.5[11]
12. Explosion lower limit (%): 7.5 [12]
13. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, miscible in ethanol, ether, acetone, and benzene. [13]
14. Relative density (25?, 4?): 1.2281
15. Solubility parameter (J·cm– 3)0.5: 22.348
16. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1 ): 7.470×109
17. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 50.720
18. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 163.6
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rat inhalation LDL0: 250ppm/7H; rat subcutaneous LD16: 560mg/kg; mouse oral LC50: 240mg/kg; mouse inhalation LC50: 1 mg/m3/2H; mammals Oral LD50: 240mg/kg;
2. The vapor is toxic and is harmful if inhaled or taken. Strongly irritating to eyes, mucous membranes and skin.
3. Acute toxicity[14]
LD50: 240mg/kg (mouse Oral)
LC50: 1000mg/m3 (mouse inhalation, 2h)
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data yet
2. Biodegradability[15] MITI-I test, the initial concentration is 100ppm, the sludge concentration is 30ppm, and the degradation is 32%~75% after 4 weeks.
3. Non-biodegradability No information available
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 22.57
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 92.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 214.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 28.4
5. Polarizability: 8.94
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.7
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3.?Number of ? bond receptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: None
6. Topological molecules Polar surface area 26.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 52.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Number of determined atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Number of uncertain atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determined number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[16] Stability
2. Incompatible substances[17] Acids, alkalis, strong oxidants, strong reducing agents
3. Conditions to avoid contact[18] Heat
4. Polymerization hazard[19] No polymerization
5. Decomposition products[20] Hydrogen chloride
Storage method
Storage Precautions[21] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 32°C and the relative humidity should not exceed 80%. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, acids, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency spill treatment equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Prepared by esterification reaction of chloroacetic acid and methanol. Mix methanol and chloroacetic acid evenly at a weight ratio of 0.366:1, stir and heat, and perform esterification reaction at 105-110°C. During the reaction process, the ternary azeotrope of methyl chloroacetate, water and methanol is continuously steamed out, and is separated into layers through the ester separator. The separated methanol and water are returned to the reaction pot, and the separated crude ester is treated with sodium carbonate. neutralize. The neutralized crude ester is first distilled under normal pressure to cut the 130°C fraction, and then distilled under reduced pressure to collect the 65°C (8kPa) fraction, which is the finished product of methyl chloroacetate. The yield is about 96%. When used as a pesticide intermediate, the crude ester obtained can be washed and neutralized to obtain a product with a content of more than 95%, which can be used directly. To produce 1 ton of methyl chloroacetate of this specification, approximately 800kg of chloroacetic acid and 330kg of methanol are consumed. During laboratory preparation, concentrated sulfuric acid is often added dropwise to the mixture of chloroacetic acid and methanol, heated to reflux for 5 hours, and then neutralized, washed, dried, and distilled under reduced pressure to obtain the finished product.
2. Its preparation method is through esterification reaction of chloroacetic acid and methanol.
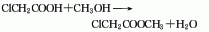
Place methanol and chloroacetic acid by mass Mix evenly at a ratio of 0.336:1, stir and heat, and perform esterification reaction at 105 to 110°C. During the reaction process, the ternary azeotrope of methyl chloroacetate, water and methanol is continuously steamed out, and is separated into layers through the ester separator. The separated methanol and water are returned to the reaction pot, and the separated crude ester is treated with sodium carbonate. neutralize. The neutralized crude ester is first distilled under normal pressure to cut the 130°C fraction, and then distilled under reduced pressure to collect the 65°C/79.98kPa fraction to obtain the finished product of methyl chloroacetate with a yield of about 96%.
3.Add chloroacetic acid and methanol into the enamel jar, heat to dissolve, cool, add concentrated sulfuric acid dropwise, heat to reflux for 5 hours, after cooling, Wash twice with water, twice with 5% sodium carbonate, then wash with water until ph=7, separate the aqueous layer and dry it with anhydrous magnesium chloride, filter out the desiccant, and distill under reduced pressure to obtain the finished product.

Purpose
Used in organic synthesis and as an intermediate for the pesticide “dimethoate”. [22]
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/43001extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/catalyst-a-300/extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/semi-rigid-foam-catalyst-tmr-4-dabco-tmr/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/pc-cat-nem-catalyst-n-ethylmorpholine/extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/benzyldimethylamine/extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/dabco-bl-13-niax-a-133-jeffcat-zf-24/extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/delayed-catalyst-1028-delayed-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/flexible-foams-catalystextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44024extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40214