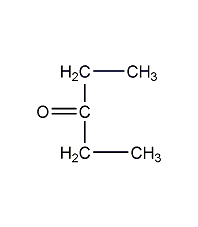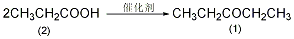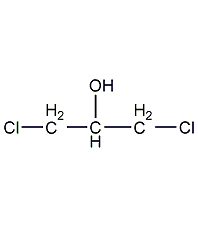
Structural formula
| Business number | 02AS |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H6Cl2O |
| Molecular weight | 128.99 |
| label |
?,?-dichloroglycerol, CH2ClCH(OH)CH2Cl, Glycerol-?,?-dichlorohydrin, sym-Dichloroisopropyl alcohol, Dichlorohydroxypropane, Solvents for nitrocellulose spray paints, paints and varnishes, celluloid adhesive |
Numbering system
CAS number:96-23-1
MDL number:MFCD00000951
EINECS number:202-491-9
RTECS number:UB1400000
BRN number:1732063
PubChem number:24862332
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless and transparent liquid with ether smell.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4?): 1.3587
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 4.45
4. Melting point (ºC): -4
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 176
6. Refractive index (n20ºC): 1.4837
7. Flash point (ºC): 73.9
8. Vapor pressure (kPa, 28ºC): 0.13
9. Solubility: 11% dissolved in water at 19?. Miscible with alcohol and ether. Soluble in vegetable oils and most organic solvents.
10. Relative density (20?, 4?): 1.3638
11. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.4817
12. The liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -385.3
Toxicological data
1. Skin/eye irritation: Open irritation test: rabbit, skin contact: 10mg/24H, severity of reaction: mild.
2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 110mg/kg; rat inhalation LCLo: 125ppm/4H; mouse oral LD50: 25mg/kg; rabbit skin contact LD50: 800?L/ kg;
3. Chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity: Rat oral TDLo: 4550mg/kg/2Y-C;
4. Mutagenicity: Microbial Salmonella typhimurium mutation: 1 ?mol/plate; E. coli mutation: 30 ?mol/tube;
Hamster lungs Sister chromosome exchange: 250?mol/L;
5. It is a moderately toxic species and can easily invade the body through the respiratory tract and skin. Acute poisoning may occurDizziness, drunkenness, and drowsiness. A few hours later, epigastric pain, vomiting, increased body temperature, confusion, and decreased urine output occurred. Symptoms such as nasal and oral mucosa and subcutaneous bleeding, mild yellowing of the skin all over the body, fast and thin pulse, and drop in blood pressure may subsequently occur. TJ 36-79 stipulates that the maximum allowable concentration in workshop air is 5 mg/m3.
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 27.13
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 98.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 242.5
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 36.4
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 10.75
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.8
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 20.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 28
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid contact with strong acids, strong oxidants, strong reducing agents, acid chlorides, and acid anhydrides. In case of fire, it produces highly toxic phosgene. It is highly hygroscopic and releases hydrogen chloride quickly when it encounters water. Non-corrosive to metals when dry.
Chemical properties: 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol rapidly removes hydrogen chloride in alkaline solution to generate 3-chloro-1,2-epoxypropane. Oxidation with sodium dichromate and sulfuric acid produces ?, ??-dichloroacetone. Oxidation with concentrated sulfuric acid produces chloroacetic acid. Heating in excess ethanol and sodium hydroxide solution produces 1,3-diethoxy-2-propanol.
Storage method
Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the reaction of propylene chloride and hypochlorous acid.
2. Obtained from the reaction of glycerol and hydrogen chloride in the presence of glacial acetic acid. Raw material consumption quota: glycerol 796kg/t, hydrogen chloride 781.2kg/t, glacial acetic acid 66.2kg/t.
Refining method: vacuum distillation and refining.
3. Preparation method:
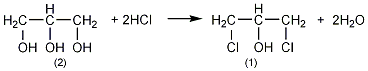
Add 90% glycerol (2) 500g (4.9mol) and 10g acetic acid into the weighed reaction bottle, install a vent tube deep into the bottom of the bottle, heat the oil bath, and control the temperature of the oil bath to 100 ~110?. Dry hydrogen chloride gas (prepared by the reaction of ammonium chloride and sulfuric acid) is introduced. Hydrogen chloride gas is absorbed quickly at the beginning, and gradually slows down over time. When the mass increases by about 440g, stop flowing hydrogen chloride gas. After cooling, the hydrogen chloride is extracted under reduced pressure. Slowly add solid sodium carbonate to neutralize the acid in the reaction system until it becomes weakly alkaline. Water can be added appropriately to facilitate the reaction with sodium carbonate, about 200mL of water. The water layer was separated, and then distilled under reduced pressure to collect the fraction below 68°C/1.65kPa (about 110g) and the fraction between 68 and 75/1.65kPa (about 385g). The water in the first fraction is removed and re-distilled, and the 68-75/1.65kPa fraction is collected to obtain about 50g of product. The product of this fraction was re-distilled, and the fraction of 70~73/1.65kPa was collected to obtain 350g of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol ?(1), with a yield of 55%. Note: ? 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol can also be prepared by reacting allyl chloride and hypochlorous acid. The reaction formula is as follows. [1]
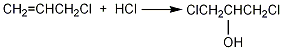
Purpose
Used in the synthesis of the antiviral drug ganciclovir, used as a solvent for cellulose acetate and ethyl fiber, and also used in the manufacture of epoxy resin, ion exchange resin, etc. Used as solvent for nitrocellulose spray paint, paint, varnish, and celluloid adhesive. Also used to prepare ion exchange resin and 3-chloro-1,2-epoxypropane, etc.
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/tetramethyldipropylene-triamine-cas-6711-48-4-bis-3-dimethylpropylaminoamine/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/38916extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/2-methylcyclohexylamine/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/45231extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/di-n-butyl-tin-diisooctoate-cas2781-10-4-fascat4208-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/catalyst-a-300/extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/high-quality-bismuth-octoate-cas-67874-71-9-bismuth-2-ethylhexanoate/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/644extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44594extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/103-83-3/